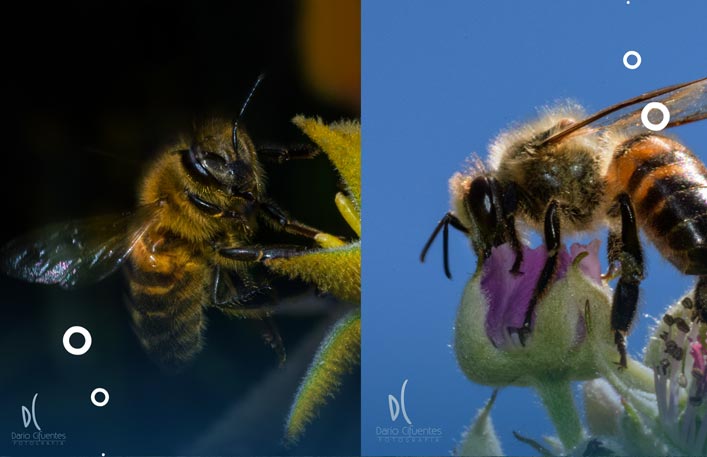
Did you know that bees not only produce honey, but are also excellent pollinators? Did you also know that the smallest bee in the world measures only 2mm and the largest can measure up to 4cm?
In this article you will know a little more about bees and you will learn that they not only live in hives, but you can find them anywhere in the world, except in Antarctica. And it’s not because they don’t like the cold, but because there are no plants to pollinate and no food for their survival.
You can find different types of bees, wild bees and bees that live in hives, which are about 60,000 approximately, although it sounds quite a significant number does not mean that our pollinator friends are not in danger of extinction. And not only that, but there are also more than 20,000 species of bees and 85% of them do not live in hives and are solitary.
Learn more about bees, why they are endangered and how you can help them in this article.
Why do we depend on bees?
The mission of bees on planet earth is very important, they along with bats, butterflies, hummingbirds, some insects and animals, help in pollination. Thanks to this process, diversity in ecosystems can survive, along with the production and survival of many wild plants and crops.
Simply put, we depend on bees for our food security as 75% of agricultural crops are achieved through pollination.
Their life expectancy depends on the type of feeding. Queen bees can live about 5 years, drones approximately 100 days and worker bees between 45 to 52 days.

Is their survival at risk?
Bees are in danger of extinction due to monocultures, fertilizers, intensive agricultural practices, pesticides, invasive species, diseases such as mites, fungi, viruses, pests and climate change.
Wild bees are most at risk because they do not live in hives and sometimes tend to be alone. They like to nest in mud structures, snail shells, abandoned nests of other insects and in some plants.
Some of these bees are very selective with food, over time they have adapted to different plants and a few only feeds on a specific plant. This becomes a problem because humans have intervened by transforming much of the environment for their own convenience, eradicating or moving food that is only found in certain areas, changing it for agricultural industrialization and monocultures.
However, honeybees are also at risk, as both have to face several challenges. Let’s find out what they are:
– In agronomic practices, there is an improper use of pesticides, intensive cultivation that diminishes the habitat and food of several pollinators.
– Climate change has caused chaos in the seasons of some countries, lengthening the time of the seasons. Countries in the tropics are also often affected as nectar and pollen collection is interrupted, affecting the work of bees and damaging their colonies and offspring.
– Genetic modification has also affected bees, because it selects them more for honey productivity, reducing their genetic diversity, making them more vulnerable to diseases and parasites, and weakening queen bees.
– Varroa mites are the greatest enemies of honey bees, as they adhere to them and weaken them. They are also transmitters of viral diseases, putting the entire hive at risk, but not only this parasite weakens them, there are also predators such as the Asian hornet and other pests that cause diseases caused by bacteria, viruses and fungi.
-Destruction of their habitat or change of plant species that are not from the area, leaving the bees without food and homeless.
There is hope
It is possible that bees and other pollinators return and grow in numbers, one of the solutions is to stop using toxic products, exercise controls on pesticides, change aggressive crops and be more environmentally friendly by preserving the area’s own crops, adopting an ecological agriculture where the environment is not contaminated with chemicals, considering the health of people and pollinators.
Generate a wildflower corridor on agricultural land, preserving the diversity of different bee species.
You can be part of the change
Due to human impacts, extinction rates have increased from 100 to 1,000 times higher than normal. About 35% of invertebrate pollinators such as bees and butterflies and 17% of vertebrate pollinators such as bats are globally threatened with extinction.
In order to slow the decline in these species you can make a change in your daily life. – Buy and support farmers who carry out sustainable agricultural practices.
– Help care for and maintain forest ecosystems.
– Share this article with everyone you know who wants to know more about bees.
– Grow different varieties of native plants that bloom at different times of the year.
Farmers and beekeepers can modify and reduce the use of pesticides, create natural barriers with local trees and plants, reserve and care for some areas as natural habitat, respect bee nesting sites.
We must raise awareness of what is happening to bees and other pollinators, their lives and ours are at stake. Let’s take care of this majestic blue planet and be part of the change.
The time is now, raise awareness of their situation by sharing this information on your social networks and in your circle of friends.
Don’t forget to follow us on social networks like Instagram and Facebook for more content and ideas to take care of our planet.